Gin 使用示例(二十一):模型绑定和验证
可以使用模型绑定将请求数据绑定到类型,Gin 支持绑定 JSON、XML、YAML 以及标准的表单数据。
Gin 框架默认使用 go-playground/validator.v8 对数据进行验证。
你需要在所有需要绑定的字段上设置相应的绑定标签,例如,如果绑定数据来自 JSON,需要设置 json:"fieldname"。
Gin 框架提供了两种绑定方案:
- Must Bind
- 方法:Bind, BindJSON, BindXML, BindQuery, BindYAML
- 行为:这些方法会调用底层的
MustBindWith方法,如果出现绑定错误,会通过c.AbortWithError(400, err).SetType(ErrorTypeBind)退出请求,如果你想要对该行为有更多的控制,请使用下面 Should Bind 这套方案
- Should Bind
- 方法:ShouldBind, ShouldBindJSON, ShouldBindXML, ShouldBindQuery, ShouldBindYAML
- 行为:这些方法会调用底层的
ShouldBindWith方法,如果出现绑定错误,需要开发者自己来处理
当使用上述绑定方法时,Gin 框架会根据请求头 Content-Type 推断绑定方案,如果你对要绑定的类型非常确定,可以直接使用 MustBindWith 或 ShouldBindWith 方法。
你还可以通过 binding:"required" 标签来指定哪些字段是必需的,如果必需字段为空会报错,示例代码如下(src/gin-demo/examples/model_binding.go):
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
// Binding from JSON
type Login struct {
User string `form:"user" json:"user" xml:"user" binding:"required"`
Password string `form:"password" json:"password" xml:"password" binding:"required"`
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
// Example for binding JSON ({"user": "manu", "password": "123"})
router.POST("/loginJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
var json Login
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&json); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
if json.User != "xueyuanjun" || json.Password != "123456" {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{"status": "unauthorized"})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": "you are logged in"})
})
// Example for binding XML (
// <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
// <root>
// <user>user</user>
// <password>123</password>
// </root>)
router.POST("/loginXML", func(c *gin.Context) {
var xml Login
if err := c.ShouldBindXML(&xml); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
if xml.User != "xueyuanjun" || xml.Password != "123456" {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{"status": "unauthorized"})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": "you are logged in"})
})
// Example for binding a HTML form (user=manu&password=123)
router.POST("/loginForm", func(c *gin.Context) {
var form Login
// This will infer what binder to use depending on the content-type header.
if err := c.ShouldBind(&form); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
if form.User != "xueyuanjun" || form.Password != "123456" {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{"status": "unauthorized"})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": "you are logged in"})
})
// Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080
router.Run(":8080")
}
运行上述代码启动服务器:

在终端窗口通过 curl 模拟访问:
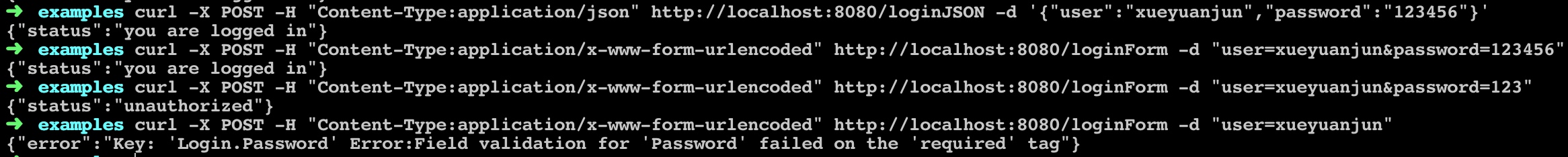
如果要跳过验证,对应字段的 binding 属性设置为忽略即可:
binding:"-"
无评论