员工 API 开发(下)
获取员工列表
在上篇教程中,学院君给大家演示了员工创建 API 的开发,今天我们来接着完成它的姊妹篇 —— 获取员工信息的 API 开发。这里,我们将遵循 JSON API 的规范完成员工查询、嵌套关联及过滤:
# 返回邮箱中包含 john@example.com 的所有员工
GET /api/v1/employees?filter[email]=john@example.com
# 返回姓名中包含 freek & 职位中包含 developer 的所有员工
GET /api/v1/employees?filter[full_name]=freek&filter[job_title]=developer
# 返回部门名称中包含 development 的所有员工
GET /api/v1/employees?filter[department.name]=development
# 返回员工时包含部门信息,避免 N+1 查询问题
GET /api/v1/employees?include=department
底层将基于 Laravel Query Builder 扩展包实现,这个已经在项目初始化的时候安装过了。
测试用例
我们从测试用例开始,新建一个 GetEmployeesTest 测试文件,并编写两个测试用例,一个用于测试部门员工列表获取,一个用于测试过滤器筛选功能:
<?php
use App\Enums\PaymentTypes;
use App\Models\Department;
use App\Models\Employee;
use App\Models\User;
use Laravel\Sanctum\Sanctum;
use function Pest\Laravel\getJson;
// 测试部门员工列表
it('should return all employees for a department', function () {
Sanctum::actingAs(User::factory()->create(), ['*']);
$development = Department::factory(['name' => 'Development'])->create();
$marketing = Department::factory(['name' => 'Marketing'])->create();
$developers = Employee::factory([
'department_id' => $development->id,
'payment_type' => PaymentTypes::from('salary')->value,
])->count(5)->create();
Employee::factory([
'department_id' => $marketing->id,
'payment_type' => PaymentTypes::from('hourlyRate')->value,
])->count(2)->create();
$employees = getJson(route('department.employees.index', ['department' => $development]))
->json('data');
expect($employees)->toHaveCount(5);
expect($employees)
->each(fn ($employee) => $employee->id->toBeIn($developers->pluck('uuid')));
});
// 测试过滤器
it('should filter employees', function () {
Sanctum::actingAs(User::factory()->create(), ['*']);
$development = Department::factory(['name' => 'Development'])->create();
$marketing = Department::factory(['name' => 'Marketing'])->create();
Employee::factory([
'department_id' => $development->id,
'payment_type' => PaymentTypes::from('salary')->value,
])->count(4)->create();
$developer = Employee::factory([
'full_name' => 'Test John Doe',
'department_id' => $development->id,
'payment_type' => PaymentTypes::from('salary')->value,
])->create();
Employee::factory([
'department_id' => $marketing->id,
'payment_type' => PaymentTypes::from('hourlyRate')->value,
])->count(2)->create();
$employees = getJson(
route('department.employees.index', [
'department' => $development,
'filter' => [
'full_name' => 'Test',
]
])
)->json('data');
expect($employees)->toHaveCount(1);
expect($employees[0])->id->toBe($developer->uuid);
});
业务代码
然后编写业务代码让测试用例通过,调整 EmployeeResource 将返回的 Id 换成 Uuid:
class EmployeeResource extends JsonApiResource
{
...
public function toId(Request $request): string
{
return $this->uuid;
}
}
然后编写 DepartmentEmployeeController 的 index 方法用于返回部门员工列表数据,这里我们通过 QueryBuilder 查询部门员工信息,并通过 allowedFilters 方法设置允许通过用户名、职位、邮箱字段进行过滤筛选(后面要用到),最后通过 EmployeeResource 封装员工数据,使其满足 JSON API 规范:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Http\Resources\EmployeeResource;
use App\Models\Department;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Spatie\QueryBuilder\QueryBuilder;
class DepartmentEmployeeController extends Controller
{
public function index(Request $request, Department $department)
{
$employees = QueryBuilder::for(Employee::class)
->allowedFilters(['full_name', 'job_title', 'email'])
//->where('department_id', $department->id)
->whereBelongsTo($department) // 和上面的查询等价
->get();
return EmployeeResource::collection($employees);
}
}
在 routes/api.php 中新增部门员工列表路由入口:
use App\Http\Controllers\DepartmentEmployeeController;
Route::get(
'departments/{department}/employees',
[DepartmentEmployeeController::class, 'index']
)->name('department.employees.index')
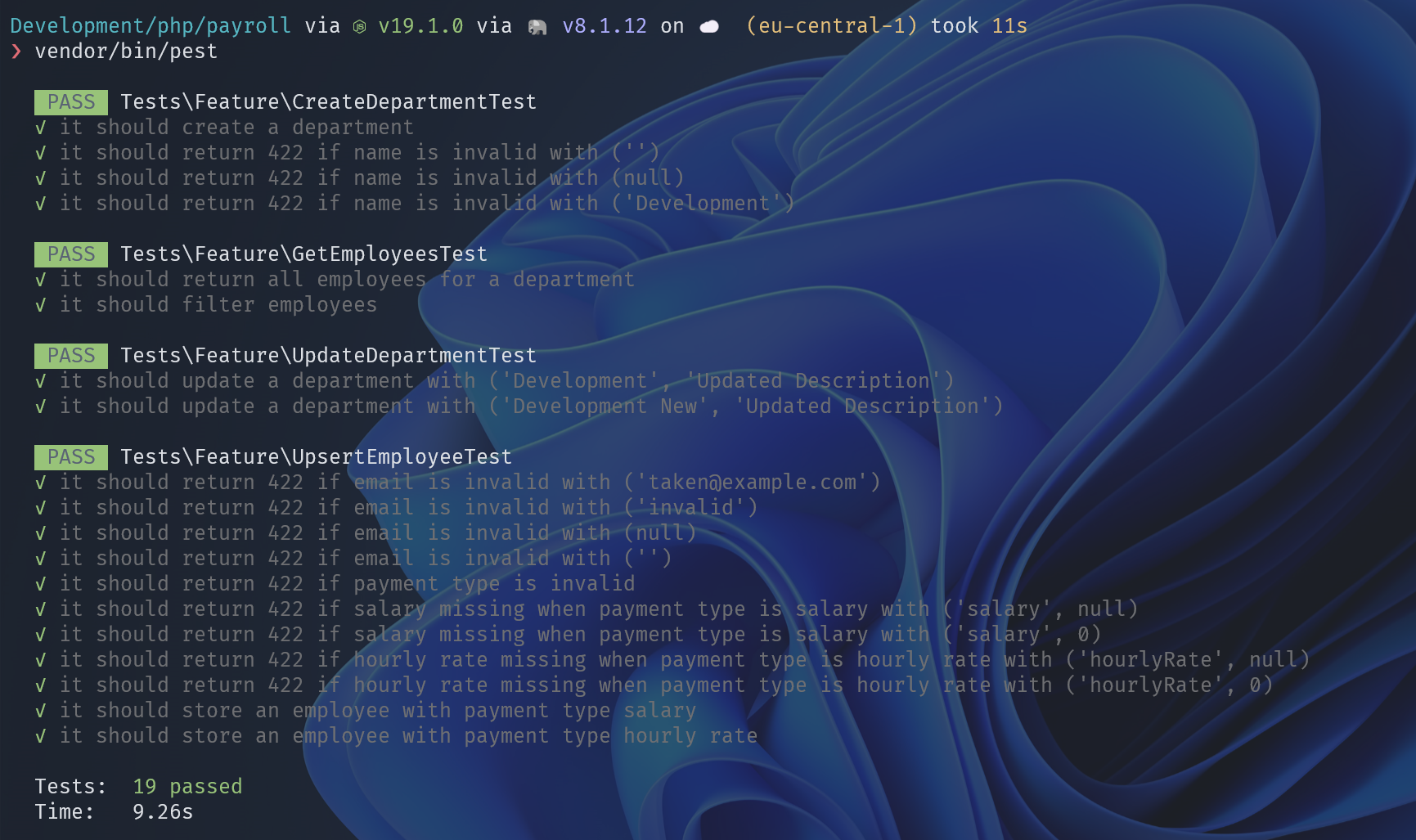
让测试用例通过
运行测试命令,测试通过,表明我们的部门员工列表和筛选器功能正常:
关于 Laravel Query Builder 的更多使用方法可以参考之前的教程,这里不一一展示了。
资源和值对象
基本功能 OK 之后,又到了代码优化和重构环节,这里我们将使用值对象的方式对薪资金额的数据格式进行优化。
所谓值对象,就是封装了基本标量数据(整型、浮点型、字符串、布尔类型等)的低级类,以薪资金额为例,我们通过一个 Money 值对象对其进行封装:
<?php
namespace App\VOs;
class Money
{
public function __construct(private readonly int $valueInCents)
{
}
// 对外提供静态方法进行构建
public static function from(int $valueCents): self
{
return new static($valueCents);
}
// 转化为美元格式
public function toDollars(): string
{
return '$' . number_format($this->valueInCents / 100, 2);
}
// 金额数值(以分为单位,避免浮点运算对精度的丢失)
public function toCents(): int
{
return $this->valueInCents;
}
}
然后我们就可以将其应用到 EmployeeResource 资源类中,编写可读性更好的返回数据格式:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Resources;
use App\VOs\Money;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use TiMacDonald\JsonApi\JsonApiResource;
class EmployeeResource extends JsonApiResource
{
/**
* Transform the resource into an array.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return array|\Illuminate\Contracts\Support\Arrayable|\JsonSerializable
*/
public function toAttributes($request): array
{
return [
'name' => $this->full_name,
'email' => $this->email,
'jobTitle' => $this->job_title,
'payment' => [
'type' => $this->payment_type->type(),
'amount' => [
'cents' => Money::from($this->payment_type->amount())->toCents(),
'dollars' => Money::from($this->payment_type->amount())->toDollars(),
],
],
];
}
public function toId(Request $request): string
{
return $this->uuid;
}
}
当然,我们可以对 Money 值对象进一步进行封装,让资源类中的调用代码更精简:
<?php
namespace App\VOs;
class Amount
{
public function __construct(private readonly Money $cents, private readonly Money $dollars)
{
}
public static function from(int $valueInCents): self
{
return new static(Money::from($valueInCents), Money::from($valueInCents));
}
public function toArray(): array
{
return [
'cents' => $this->cents->toCents(),
'dollars' => $this->dollars->toDollars(),
];
}
}
<?php
namespace App\Http\Resources;
use App\VOs\Amount;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use TiMacDonald\JsonApi\JsonApiResource;
class EmployeeResource extends JsonApiResource
{
/**
* Transform the resource into an array.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return array|\Illuminate\Contracts\Support\Arrayable|\JsonSerializable
*/
public function toAttributes($request): array
{
return [
'name' => $this->full_name,
'email' => $this->email,
'jobTitle' => $this->job_title,
'payment' => [
'type' => $this->payment_type->type(),
'amount' => Amount::from($this->payment_type->amount())->toArray(),
],
];
}
public function toId(Request $request): string
{
return $this->uuid;
}
}
可以看到,值对象有以下特点:
- 不可变,属性值只读,不提供 setter
- 不包含任何标志性属性,如 ID(这也是值对象与实体的主要区别)
在应用代码中,通常我们可以将地址、邮箱、数字等标量数据转化为值对象进行处理。通过使用值对象,可以从内聚的标量数据中创建对象,因此,使用值对象有如下优点:
- 让代码更高级
- 澄清事实避免混淆(通过代码可以直观看出这个值的用途)
- 可以封装对空值的处理
其实涉及到数据处理的操作在业务系统多个地方都会用到,值对象通常应用在应用内部,而在应用边界,通常使用数据转换对象(DTO)。
好了,到这里,我们的员工 API 开发就告一段落了,下篇教程,我们将进入最后一个功能模块 —— 支付 API 的开发。本项目的代码已经提交到 Github,需要的话可以自行去查阅:https://github.com/geekr-dev/payroll。

1 条评论